Having just recently finished the localization process of some of my English Adwords campaigns into European languages, I thought I’d share some things I learned along the way. After considerable effort and reorganization the campaign is succeeding, but it was fraught with failure and ‘lessons learned’. Hopefully some of my experiences will be helpful if you’re thinking of translating your campaigns to target new markets and languages…
Having just recently finished the localization process of some of my English Adwords campaigns into European languages, I thought I’d share some things I learned along the way. After considerable effort and reorganization the campaign is succeeding, but it was fraught with failure and ‘lessons learned’. Hopefully some of my experiences will be helpful if you’re thinking of translating your campaigns to target new markets and languages…
Surveying the Competitive Landscape
Before going through the work of translating my English campaigns into the most common European languages, I took a look at the competitive landscape via Google’s much-improved Ad Preview Tool (remember to set both the country to the locale you’re after, but also the language selection). I was looking for a few things in surveying the competition in each country:
- Were the competitors in the various markets were English vendors using translated campaigns, or companies native to those locales?
- If the competitors were English, was their translation properly done by native speakers, or just a quick Google Translate?
- Again if the competitors were English, was their entire end-to-end process properly localized, from keywords to ads to landers to e-commerce and customer support?
- If the competitor was a local, how aggressive were their PPC ads, landers, shopping cart and the like from a conversion optimization perspective?
The basic idea here was this: “Is this going to be like shooting fish in a barrel if I’m highly optimized, or do the competitors have strong PPC fu?”
It turns out that in most countries my competitors in this particular niche were typically other English vendors with Google-translated ads, landing pages, and completely untranslated e-commerce checkout setup.
Finding a Translator and Where to Start?
Now that I knew which countries and languages to start localizing for (in order of local search volume primarily), I needed to decide where to begin. I had decided to do a full end-to-end localization from keywords to e-commerce and customer support. I also knew that I wanted my translated content to be as close to 100% accurate as possible.
To test just how good or bad Google translate was, and to help evaluate the proper translation, I put an ad on Craigslist for a fully bilingual translator who was born and raised in the first country I decided to test. To qualify the applicants, I gave them a sizeable snippet of text from one of my existing landing pages and ask them to email me back their translation from English into the chosen language.
I have a friend who certainly qualifies to do proper translation but wasn’t looking to be a translator for this project to evaluate the control text in English, and then the submitted translation in the new language. To make things more interesting, I translated the English snippet using Google translate and included that for review as well.
The results were interesting. Five candidates had submitted translated snippets, plus the version made with Google Translate. Oddly, three of the five candidates submitted results identical to the Google Translate version:) Disregarding those, I forwarded on the remaining two real translations. My friend sent back one saying it was the most accurate, and represented the way a local would translate the English snippet. The other had spelling errors and other grammatical issues and was disregarded. And the Google Translate version? To say it had butchered the translation would be an understatement.
The point? There’s a big difference between Google Translate’s “good enough” on-the-fly translation to help you quickly understand the odd alternate language site, but for heaven’s sake don’t use it to translate your ads and landing pages.
Translation Gotchas & Efficiency
Now that we had a translator, we set her to work (on an hourly basis, in our local offices) on translating the keywords first, then the Adwords ads, then the landing pages, then the shopping cart, then the receipts and customer support touch points.
One thing I learned very quickly is that English does not always have a one-for-one equivalent in other languages. In fact, you have to watch out for tenses of words as well, as often the past/present can be tricky and change the meaning of keywords and ads if you’re not careful. Same goes for plurals.
Though overall the process of finding someone locally to do the translation, vetting them, and then working with them at your offices worked really well. When you realize the amount of back and forth and questions the translator may have to clarify the meaning of what you’re promoting (particularly with technical terms and the like) I highly recommend not trying to do the entire process over email. There’s just too much interaction required in my experience to make the email back-and-forth route efficient.
Adwords Campaign ‘Cloning Fail’
I had decided not to start a net-new campaign with entirely new keywords and ads for this project, rather I thought I’d just clone the English campaign and have it translated, then switch the language and geographic settings in Adwords Editor and reload it.
Seems logical no? Well as it turned out, it wasn’t quite so simple.
Of course copying, pasting, and translating the campaign in Adwords Editor was a snap, as was quickly adjusting the languages and country settings. What I didn’t factor in though was that even with a seasoned translator doing the heavy lifting, people just do not always search for things the same way they do in English.
It wasn’t just that they use slightly different suffix’s or word order: keywords that were the ‘high volume’ winners in both search traffic and conversion rates in English BOMBED in some of these other languages.
The best part? The clicks were still there in large volume, but they just weren’t converting. The challenge in a lot of situations was, you have this keyword, it’s getting a ton of traffic, but you can’t figure out what’s gone wrong until you first see the Search Terms report in Adwords which can take days to fully an properly populate. At first you’re looking to see if you’ve stumbled on to a term that has dual meanings, something that can easily happen in English, let alone languages you’re not familiar with.
So the keywords weren’t working the way they did in English, how about the CPCs? Turns out that simply using the (typically high) CPCs you’re used to using in your English campaigns is a BAD idea too. How bad? By the time I had things fully optimized bid-wise, I had cranked the bids down by up to 80%!
So not only are you bleeding money on keywords that aren’t working, you’re also paying 80% too much for said keywords. Not good.
Save Some Money: Learn Your Market
My advice from all of this? Do some serious research into how users in different languages and countries look for stuff online. Ask anyone and everyone you can who is from these locations originally to answer a few ‘quiz’ questions like “if you needed to find a solution for problem “X”, what would you type into Google?”
In fact, put together a Survey Monkey questionnaire and post it on Craigslist paying people a small amount from those markets (either originally or ex-pats) to fill it out and tell you they would search for refer to your product natively. This can save you HUGE dollars. In my case I blew through over $10k in ad spend before I realized I should have done this first. The same goes for just dumping a load of keywords out of a PPC spy tool and thinking that’ll cover it, you’ll end up with exactly the same problem: context.
When the dust settled and Google Analytics + the Adwords Search Terms report populated, I could see a few land mines that I had fallen onto via double-meanings etc, and also a number of negatives that were missed (to be clear, the negatives list was also translated one-for-one, but again, the correct negatives for the campaign used entirely different terms, terms I didn’t even have).
You might wonder: If the translator ‘was so good’ why didn’t she catch these things? Bottom line? That’s not really what she does. And the “what” is context. In retrospect, I needed to know the questions to ask her (see comments above under how people search for things in other countries), and I didn’t know to ask her what I didn’t know. Sounds convoluted, but basically it was my fault not hers. It’s my job to know the big picture context in my business, not hers. Lesson learned: Learn what you need to ask.
Finding the ‘Missing Piece’
Even after fixing the ‘keywords and negatives’ problems by cutting and adding new negs, the campaign still wasn’t profitable, and the keywords that were profitable were far too low in search volume to move the needle.
Why not? There was still ONE BIG problem to find and conquer before this campaign started rocking…
What was it? How did we fix it? What’s happened with the campaign since?
Usually I don’t do this with our public blog posts, but I’m going to save the answers to these for our PPCblog members. If you haven’t signed up yet, I’m running a $1 one month trial deal right now so it’ll only cost you a buck to join and get the rest of the details as well as the hundreds of pages of PPCblog members-only content.
Members have access to this, and all of our case studies, join now!
 I just wanted to give a quick heads up that PPCblog’s membership community is closing to new members starting tonight. We’ve reached our membership goal, and I want to devote more time to providing our community with resources and advice and less time to new member acquisition efforts.
I just wanted to give a quick heads up that PPCblog’s membership community is closing to new members starting tonight. We’ve reached our membership goal, and I want to devote more time to providing our community with resources and advice and less time to new member acquisition efforts.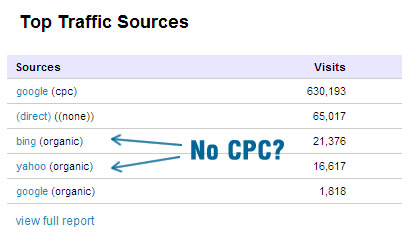
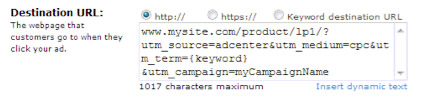













 There are reports lately of a fresh round of
There are reports lately of a fresh round of 
 Having just recently finished the localization process of some of my English Adwords campaigns into European languages, I thought I’d share some things I learned along the way. After considerable effort and reorganization the campaign is succeeding, but it was fraught with failure and ‘lessons learned’. Hopefully some of my experiences will be helpful if you’re thinking of translating your campaigns to target new markets and languages…
Having just recently finished the localization process of some of my English Adwords campaigns into European languages, I thought I’d share some things I learned along the way. After considerable effort and reorganization the campaign is succeeding, but it was fraught with failure and ‘lessons learned’. Hopefully some of my experiences will be helpful if you’re thinking of translating your campaigns to target new markets and languages…